Original Studies
SUBSTANTIATION. It is known that about 69% of all thyroid nodules undergoing surgical treatment are benign formations, and up to 75% of patients with an intermediate cytological conclusion undergo unnecessary surgical intervention. This suggests that improving the quality of differential diagnosis of nodular formations will avoid excessive economic costs for the healthcare system. In this regard, AI technologies in diagnostic algorithms for the classification of thyroid nodules were involved.
AIM. Improving the efficiency of automatic classification of thyroid nodules on ultrasound images by using a set of neural network models.
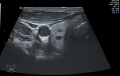
MATERIALS AND METHODS. We used ultrasound images of thyroid nodules available in open sources and obtained with the help of 3 ultrasound devices of Endocrinology Research Centre as part of Project № 22-15-00135 of the grant of the Russian Science Foundation. This article check the hypothesis that the size of the training set cannot be increased by repeating similar images from the ultrasound cine loop of one patient, but only by expanding the dataset with new unique specimens of other patients and/or data from the augmentation process.
RESULTS. As a result, a neural network model EfficientNet-B6 was proposed to solve the problem of EU-TIRADS classification of thyroid nodules based on ultrasound images of the thyroid gland.
CONCLUSION. The results obtained allow us to advance in the use of artificial intelligence methods for personalized medicine in thyroid diseases.
BACKGROUND: Studies on the relationship between thyroid autoimmunity and serum trace elements (TE) are ongoing in different parts of the world, however, the data obtained are often contradictory, which determines the relevance of this study.
AIM: The aim of the study was to identify associations between thyroid status and Anti-Thyroid Peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) with serum TE among young women.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: The study participants were 859 women aged 18–45, whose Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) was in the reference range or above 3.4 µIU/ml and with free Thyroxine (fT4) in the reference range. The exclusion criteria were the presence of menopause and decompensation of chronic diseases. The participants were subdivided into 2 groups: a group of women with TPOAb less than 30 U/ml, designated as TPOAb(-), and a group of women with TPOAb more than 30 U/m, designated as TPOAb (+). The detection of TSH, fT4, and TPOAb in serum was provided by enzyme immunoassay on the Evolis Robotized System using “Thyroid — ELISA- TSH, 0.23–3.4 µIU/ml”, “Thyroid — ELISA free T4, 10–23.2 pmol/l”, “Thyroid ELISA — TPOAb<30 U/ml” test systems. The reference values were taken from the instructions of the manufacturer Alkor Bio group (Russia). Logistic regression analysis was applied to adjudge associations between TPOAb status and serum trace elements.
RESULTS: The level of fT4 was lower in the AT-TPO (+) group compared to the AT-TPO (-), p=0.006; Triglycerides, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase was higher in the AT-TPO (+) group compared to the AT-TPO (-). There were more smoking women in the AT-TPO group (-) 4.1% versus 1.3% in AT-TPO (+). It was found that, after adjusting for likely cofounding factors, participants with antibody positivity had significantly lower concentrations of selenium; zinc, iodine, iron. When serum trace elements levels were analyzed in tertiles, the odds ratios TPOAb positivity of tertile 1 were higher that of tertile 3.
CONCLUSION: The associations between TPOAb and microelements demonstrate their involvement in autoimmune processes in the thyroid gland.
OBJECTIVES. Diffuse and nodular goiter are the most common thyroid gland (thyroid) diseases in children and adults living in iodine-deficient regions. Thyroid hormone potentiates progressive hypertrophy and hyperplasia of thyrocytes, with uneven proliferation of thyroid cells leading to nodule formation. Iodine deficiency, which promotes replication of thyroid follicular cells, also increases the incidence of TSH Receptor mutations, leading to receptor activation and autonomous functioning of follicles.
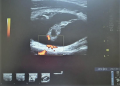
AIM. To evaluate and describe ultrasound and cytologic thyroid nodes in the regions in Russia with proven iodine deficiency.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study was conducted in regions with proven iodine deficiency in the Central and North Caucasian Federal Districts. Population of conditionally healthy adult volunteers (mean age — 47.5 years) was recruited as part of visiting events to screen for the occurrence of thyroid nodes.
RESULTS. The results obtained indicate a high prevalence of multinodular colloid goiter in adult patients living in conditions of chronic iodine deficiency. In the Chechen Republic, the prevalence of nodular thyroid pathology was found in 64.5% (205/318) of cases, and in the Tula region — in 40.6% (116/286). In the studied sample the results of cytologic examination confirmed the presence of colloid thyroid masses in 97% (60/62) — Bethesda category II; in 3% (2/62) of patients nodular masses had Bethesda IV. Diffuse goiter prevalence in the examined population was 20.8%.
CONCLUSIONS. A study indicates a high prevalence of iodine-deficient thyroid disease — multinodular colloid goiter in regions with proven chronic iodine deficiency. The wide prevalence of goiter with colloid and cystic components is confirmed by the cytologic examination with different ultrasound characteristics according to the EU-TIRADS classification. The obtained data correspond to the official statistics demonstrating high prevalence of nontoxic goiter in adults in the examined regions, which is an important argument confirming the need for systemic iodine prophylaxis.
BACKGROUND: Hypofunction of the thyroid gland in women at the pre-pregnancy stage and during pregnancy is associated with a high risk of congenital hypothyroidism in children, as a result of which irreversible changes in the nervous system are formed. Despite the mandatory intake of potassium iodide preparations, pregnant women often develop gestational hypothyroidism, which requires the appointment of levothyroxine. Many women have episodic hypofunction of the thyroid gland before pregnancy, associated with various factors. Diagnosed hypothyroidism requires hormonal correction. The recommended dose of levothyroxine calculated by the patient’s weight is not always adequate to achieve TSH targets. In addition, there are pharmacological factors. Levothyroxine sodium preparations differ in bioavailability. The stability of drugs is affected by external factors and the composition of fillers from different manufacturers of drugs.
AIM: To assess the dependence of TSH reduction on the method of taking levothyroxine in a population of pregnant women.
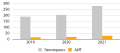
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Statistical analysis and prospective study was carried out from 2019 to 2021. On the basis of the «Perinatal Center», Tyumen, women’s consultative and diagnostic department. Pregnant women with diagnosed primary subclinical and manifest hypothyroidism in the first trimester of pregnancy (n=76) were selected for cohort observation. All pregnant women were prescribed L-thyroxine Berlin-hemi. Other levothyroxine preparations were not used in order to exclude distortion of the results of the study.
RESULTS: Pregnant women with hypothyroidism were divided into two groups according to the method of taking L-thyroxine: oral (n=54) and sublingual (n=22). A month later, TSH normalization was observed in 41 pregnant women in the oral group (76%) and in 22 pregnant women in the sublingual group (100%). Women who did not achieve hypothyroidism compensation were recommended sublingual administration without increasing the dose of L-thyroxine, provided that TSH was no higher than 4.0 mcME / ml. A TSH study a month later showed that all pregnant women achieved compensation.
CONCLUSION: Based on the conducted research, it is shown that the more rational administration of levothyroxine sodium preparations is sublingual, since there is a slightly alkaline reaction in the oral cavity, which does not have a destructive effect, like gastric juice.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2310-3787 (Online)