ORIGINAL STUDIES
BACKGROUND. Glucocorticoids are first-line drugs for the treatment of amiodarone-induced destructive thyroiditis. Due to the progression of left ventricular dysfunction, recurrence of rhythm disturbances and increased risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in this cohort of patients, rapid restoration of euthyroidism, especially in the elderly, is crucial. However, it is not always feasible with the drug therapy, because the time to achieve euthyroidism is unpredictable in each individual case. Identification of factors that allow predicting the efficacy and duration of glucocorticoid therapy will help to determine the correct tactics of patient management.
AIM. To identify factors of delayed response to glucocorticoid therapy in patients with type 2 amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The study included 11 retrospective and 22 prospective patients aged 30 to 80 years (21 men and 12 women) with verified type 2 amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis, who received prednisolone therapy at a starting dose of 30 mg/day. Anamnestic, anthropometric data, results of laboratory and instrumental diagnostics were analyzed. The follow-up period of patients was 1–5 years. The effecasy of therapy was evaluated by the time to achieve euthyroidism, duration of thyrotoxicosis, frequency of repeated waves of destruction and relapses.
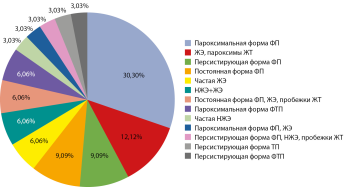
RESULTS. The average age of the patients was 57.0 [52.0; 66.0] years. After 1 month (30 days) from the start of glucocorticoid therapy, euthyroidism was achieved in 17/33 (51.5%) patients, pfT4GK-fT4GK1month<0.001, pfT3GK-fT3GK1month<0.001. Delayed achievement of euthyroidism (>30 days) was observed in 48.5% of patients. The median time to achieve euthyroidism was 72.0±3.0 (95% CI: 66.1–77.9) days, the average time was 86.9±13.4 (95% CI: 60.6–113.1) days. The median duration of thyrotoxicosis was 120.0±22.1 (95% CI: 76.6—163.4) days, the average time was 137.8±15.6 (95% CI: 107.2–168.4) days. The level of free thyroxine after 30 days of therapy depended on the interval «clinical symptoms — laboratory confirmation» (R2=0.120, p=0.049). Time to achieve euthyroidism depended on age (R2=0.185; p=0.013). Age was also a predictor of repeated waves of destruction (OR=0.833, 95% CI:0.709–0.978; R2=0.428, p=0.025).
CONCLUSION. Age is a predictive factor for the time to achieve euthyroidism in type 2 amiodarone-induced thyrotoxicosis.
BACKGROUND: the use of artificial intelligence in ultrasound diagnosis of thyroid nodules is expected and quite promising. However, in order to understand this, it is necessary to see how a doctor works with its help, diagnosing diseases step by step, and how exactly this intelligence is implemented in practical healthcare. The current publication provides an overview of existing intelligent systems for supporting medical decisions in thyroidology, and describes in detail the capabilities of the Russian intelligent computer assistant for ultrasound diagnostics - a system for stratifying thyroid nodules by EU-TIRADS categories.
AIM: increasing the accuracy and reducing the time of ultrasound diagnostics in the study of thyroid nodules through the use of an intelligent system for assisting the ultrasound doctor at various stages of his activity with demonstration of the actions of the “assistant”.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: to understand the possibilities of ultrasound doctors using artificial intelligence in their work, the proposed solution is divided into stages, each of which demonstrates the additional capabilities that a doctor has when using intelligent computer vision methods. Various artificial neural network architectures are used as an intellectual base, which can be further trained like a human on new medical data.
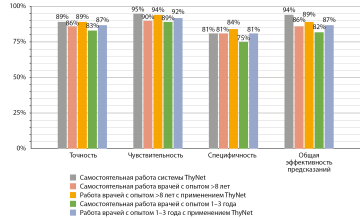
RESULTS: the proposed intelligent solution allows the ultrasound doctor to have a “second opinion” at his workplace, which, by processing ultrasound cine loops, allows him to solve the problems of segmentation and stratification of thyroid nodules according to EU-TIRADS categories with an accuracy of 70%, i.e. at the level of a doctor with 5 years of experience. The proposed data driven approach will improve its accuracy as new patient loops are processed.
CONCLUSION: the narrative leads the reader to understand in what diagnostic processes it is useful to use artificial intelligence methods in the ultrasound diagnosis of thyroid nodules, and how natural and artificial intelligence can effectively interact within the framework of a software web application.
BACKGROUND. Chronic hypoparathyroidism (HypoPT) is a relatively rare endocrine disorder. Adequate control of the disease requires the prescription of lifelong multicomponent therapy. Lack of sustained compensation of HypoPT is associated with the development of both early and delayed complications, including functional and structural renal pathology, cataracts, cerebral calcification, cardiac rhythm and/or conduction disorders, and others.
AIM. To study the associations of clinical, laboratory and instrumental parameters, as well as the medical therapy, with long-term complications of chronic HypoPT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS. The observational, continuous study was based on the data of the Russian Registry of Patients with Chronic Postoperative and Nonsurgical HypoPT; 1776 patients from 81 regions of the Russian Federation were included in the study.
RESULTS. In the study population, 26,3% of patients (n=467) had at least one of the HypoPT complications, among them nephrolithiasis/nephromicrolithiasis was diagnosed in 33,4%. Nephrocalcinosis was observed in 10,7% and was more often bilateral (93,5%). In 17,4% of patients there was a significant decrease in GFR, corresponding to CKD stages 3a-5. Cataract was present in 34,7% of patients with chronic HypoPT. Statistically significant associations were found for disease duration with impaired renal filtration function (p<0,001), nephrocalcinosis/nephrolithiasis (p=0,001) and cataract (p<0,001). Patients with impaired renal function had higher serum ionized calcium level (p=0,0071) and lower phosphorus level (p=0,002). Cataract was predominantly diagnosed in patients of older age group (p<0,001), predominant in the presence of hypocalcemia by ionized calcium level (p=0,001). In patients undergoing brain MSCT for neurological symptoms, basal ganglia calcifications were detected in more than half of the cases (56,2%). Brain calcification was associated with younger patient age (p<0,001), hyperphosphatemia (p<0,001), hypomagnesemia (p=0,010). Statistically significant associations were observed between calcification of brain structures and higher doses of alfacalcidol and calcium carbonate (p=0,007).
CONCLUSION. The analysis of the database revealed a number of associations between clinical, laboratory and instrumental parameters and long-term complications of HypoPT. The most significant factors in the development of renal pathology and cataracts are the duration of the disease, as well as off-target indicators of calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
CASE REPORTS
Parathyroid carcinoma (PC) accounts for 0.005% of all malignant neoplasms and is usually associated with an unfavourable prognosis. The greatest diagnostic difficulties arise from the atypical location of thyroid neoplasms. The prevalence of ectopic location of parathyroid gland (PG) ranges from 2 to 43%, while the incidence of this anomaly in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism is 16-30%. This article analyses the difficulties in diagnosing PC with atypical location of the thyroid gland, using two clinical cases as examples, and suggests additional methods for a personalised approach.
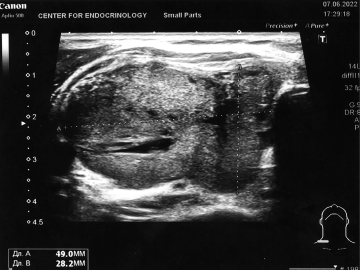
Amyloid goiter is an orphan disease characterized by the deposition of amyloid proteins in the thyroid parenchyma, which can be the result of both localized primary deposition and secondary, against the background of persistent chronic inflammatory disease. The diagnosis is made through imaging techniques and histological examination of thyroid tissue. Depending on the degree of enlargement of the thyroid gland, the presence of hypothyroidism, as well as compression syndrome, therapeutic tactics are reduced to dynamic observation, the achievement of an euthyroid state, and in case of a pronounced cosmetic defect and / or tracheal compression, surgical intervention. Histochemical staining of the resected drug is necessary to make a definitive diagnosis. The prognosis is generally favorable, but it depends on the underlying cause of amyloid deposition and the degree of thyroid damage. In this clinical case, we describe a 36-year-old patient with periodic disease, AA-amyloidosis with predominant kidney damage, after kidney allotransplantation due to a history of end-stage chronic kidney disease. The patient contacted the center with complaints of difficulty breathing, swallowing, during examination, the thyroid gland is enlarged in size, according to ultrasound data, specific changes in the thyroid gland indicate the amyloid genesis of goiter. According to the hormonal examination, it is euthyroidism. According to the cytological examination of a thyroid biopsy: extracellular deposits of a dense structureless substance colored red-brown, most corresponding to the deposition of amyloid, were found in smears of liquid cytology when stained with congo red.
REVIEW
Tumors of the thyroid gland are extremely common. The incidence of malignant thyroid neoplasms has increased rapidly in recent decades, although it is unclear whether this is a true increase or the result of widespread use of screening ultrasound. The standard diagnostic procedure for determining the risk of malignancy and indications for surgical treatment of thyroid neoplasms is fine-needle aspiration biopsy followed by cytologic examination of the cellular aspirate. Despite the fact that in the majority of cases it is possible to make a differential diagnosis between thyroid cancer and benign thyroid masses, there is a diagnostic problem with intermediate categories of cytologic findings according to Bethesda, which makes it necessary to search for alternative solutions. This determines the need to expand preoperative diagnostic possibilities. One of the key directions of work on its realization is the study of proteomic data in various thyroid pathologies. The study of the proteome of thyroid tumors opens the possibility of identifying specific protein markers or mechanisms that play a key role in the oncogenesis and metastasis of thyroid tumors, as well as potential targets for new methods of diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. All this determines the relevance and practical importance of studying thyroid pathology at the molecular level, taking into account the potential of proteins as markers.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
ISSN 2310-3787 (Online)